Vertical Internal Gear Slewing Drives: Design Principles, Load Calculation and Industrial Integration
 2026.02.23
2026.02.23
 Industry news
Industry news
Content
- 1 Mechanical Structure of Vertical Internal Gear Slewing Drives
- 2 Gear Geometry and Meshing Design
- 3 Load Analysis in Vertical Mounting Conditions
- 4 Material Selection and Heat Treatment
- 5 Sealing Systems and Environmental Protection
- 6 Installation Guidelines for Structural Stability
- 7 Maintenance and Service Life Optimization
- 8 Industrial Applications of Vertical Internal Gear Slewing Drives
Mechanical Structure of Vertical Internal Gear Slewing Drives
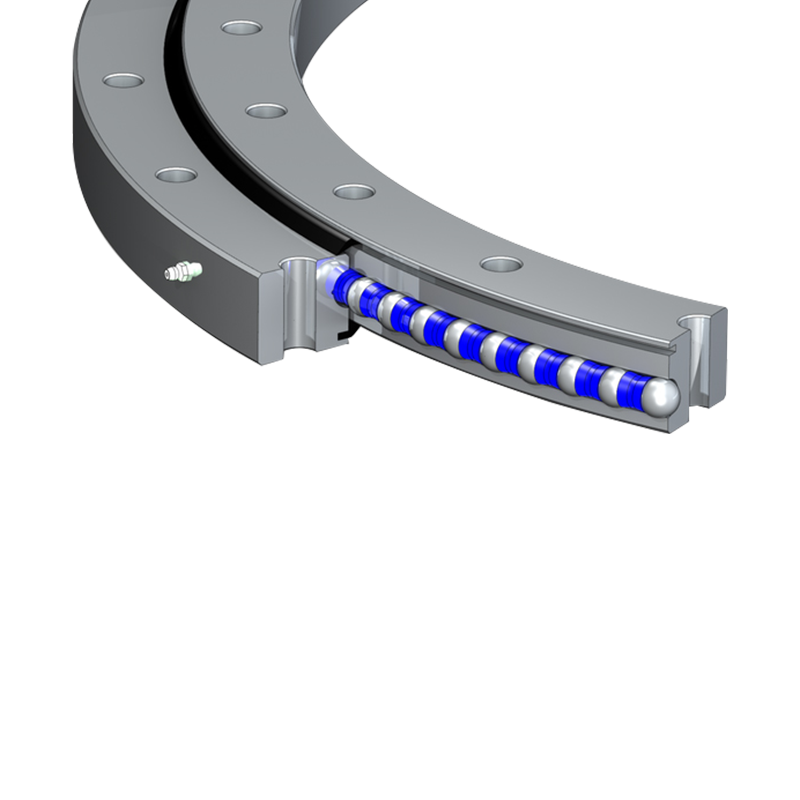
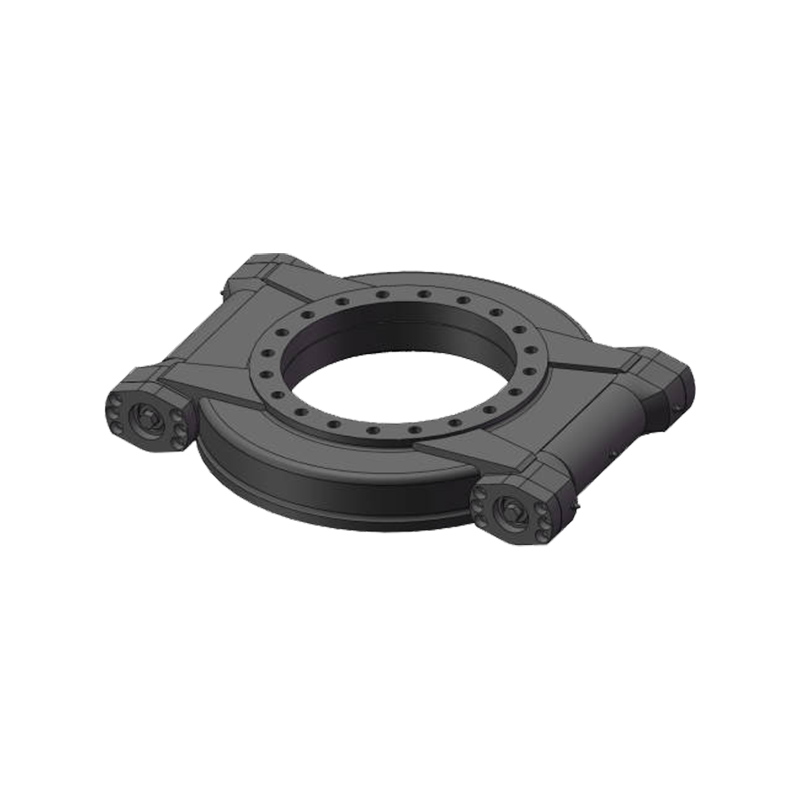
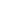
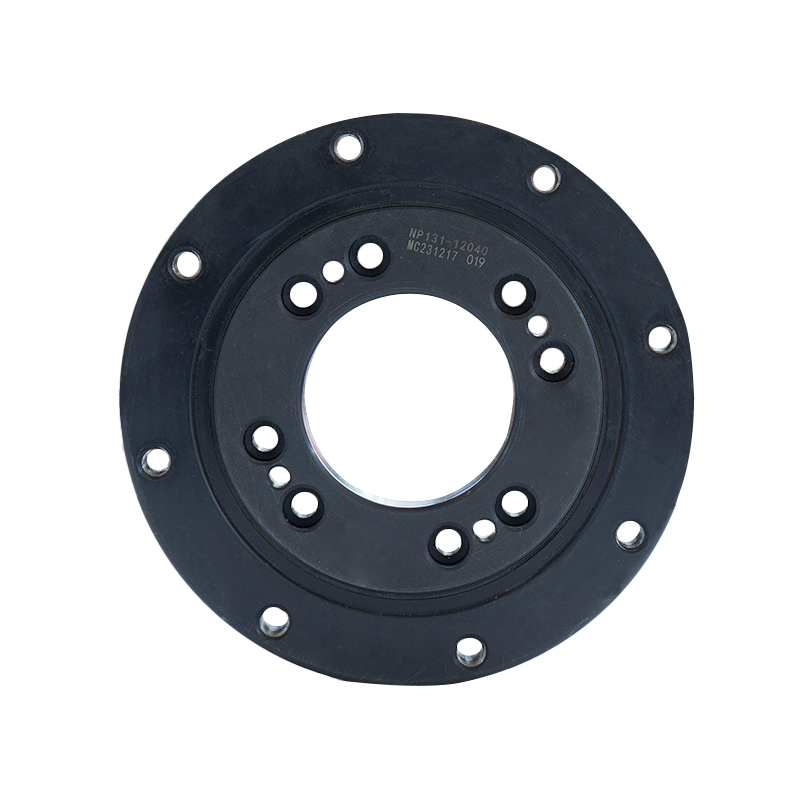
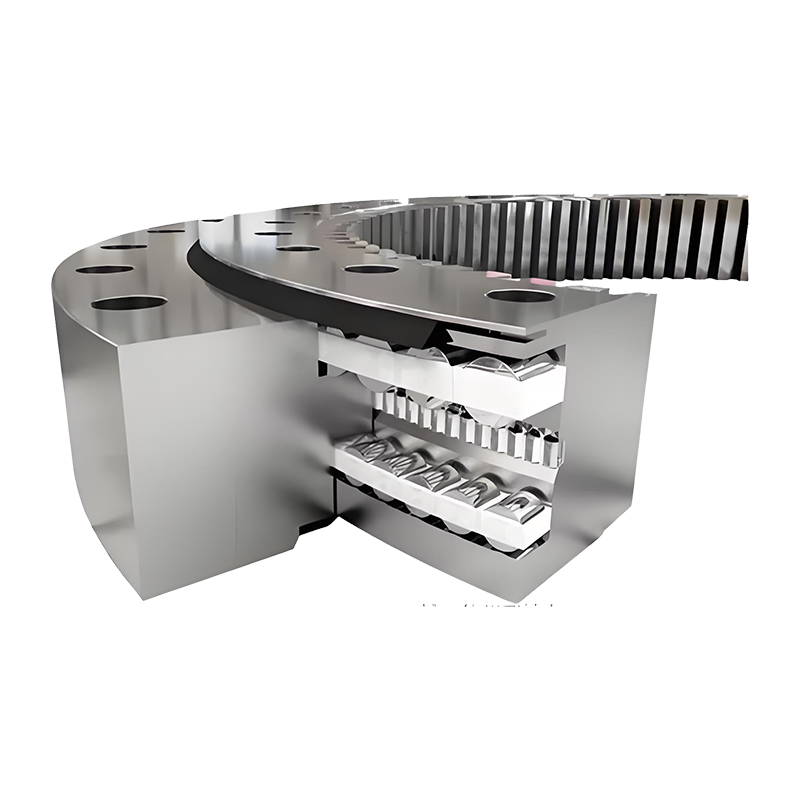
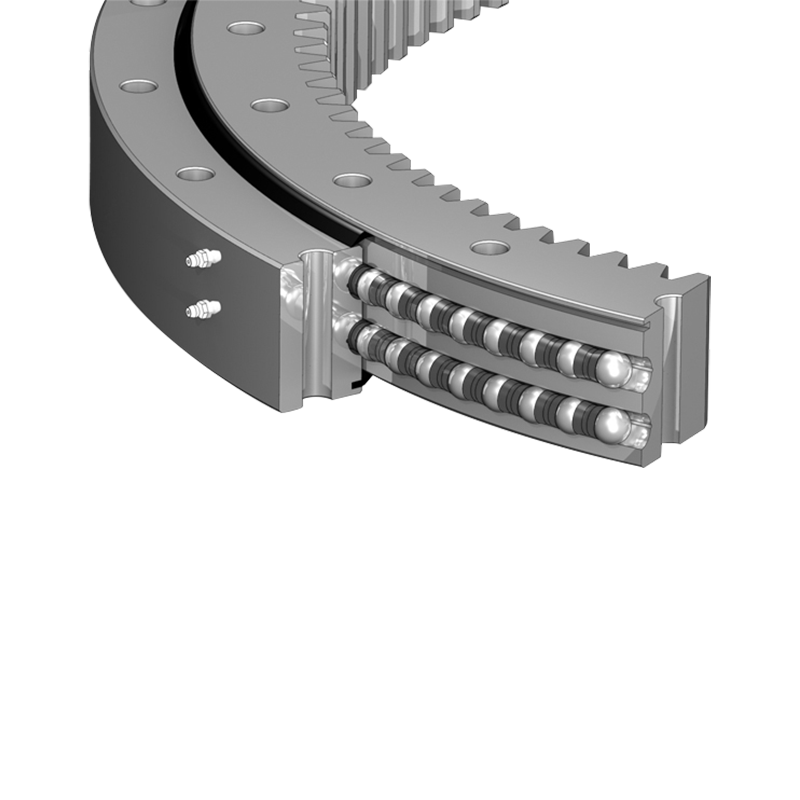
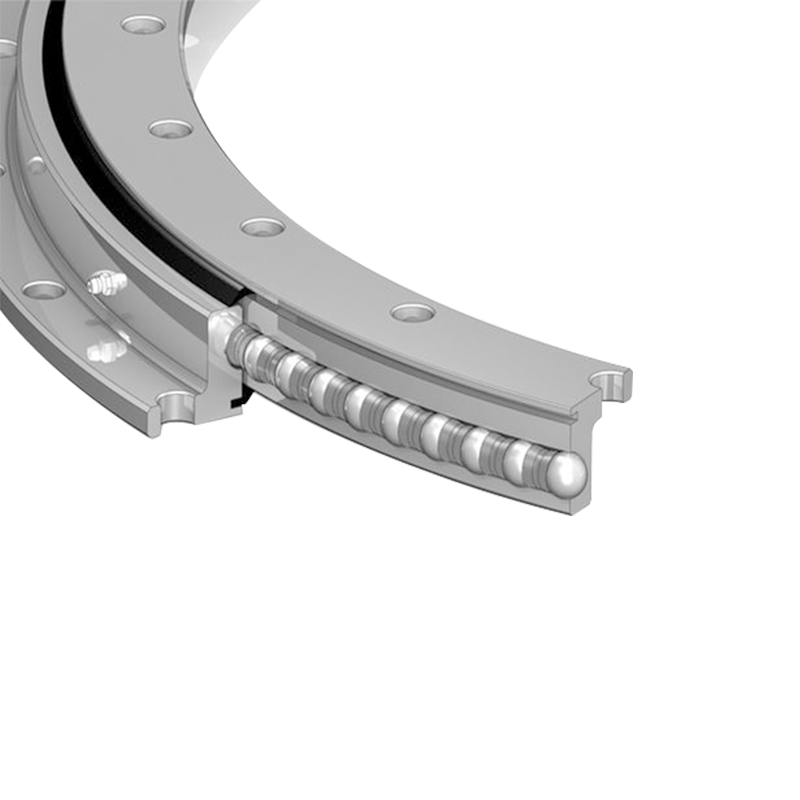
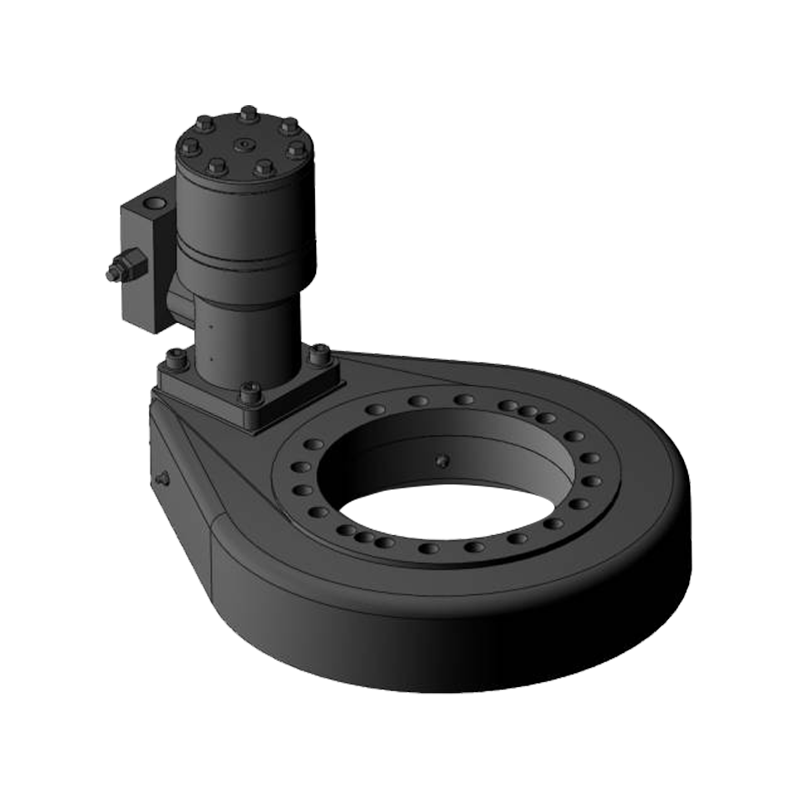
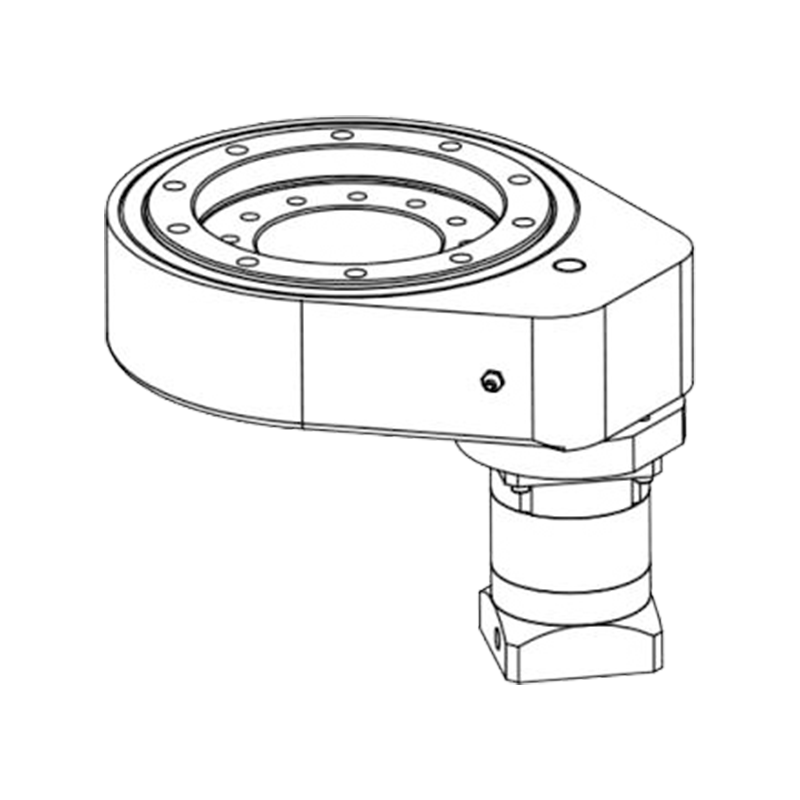
Vertical internal gear slewing drives are compact rotational assemblies designed to support heavy axial loads while delivering controlled angular motion around a vertical axis. The primary structure includes a slewing ring bearing with an internal gear profile machined into the inner ring, a worm shaft or drive pinion, a housing structure, sealing components, and mounting flanges. This configuration allows the gear teeth to remain enclosed within the ring, improving durability in demanding environments.
Unlike external gear slewing drives, the internal gear configuration positions the tooth profile inward, protecting it from mechanical impact, contamination, and corrosion exposure. The vertical arrangement is commonly selected when the rotating structure carries significant vertical weight, such as columns, rotating platforms, lifting arms, or tracking frames.
Gear Geometry and Meshing Design
Internal gear geometry directly influences torque transmission efficiency and service life. Gear modules are selected according to torque requirements, contact ratio, and expected load cycles. Higher modules increase tooth thickness and strength, while optimized involute profiles maintain smooth meshing and consistent contact pressure.
Worm-driven internal gear slewing drives offer high reduction ratios within a compact footprint. The worm shaft typically features hardened alloy steel construction with precision ground threads to ensure uniform contact. Proper backlash control prevents excessive vibration while maintaining sufficient clearance for thermal expansion.
Critical Meshing Parameters
- Gear module and pressure angle selection
- Tooth surface hardness and heat treatment depth
- Contact pattern verification during assembly
- Backlash adjustment tolerance
Load Analysis in Vertical Mounting Conditions
In vertical installations, the slewing drive must handle combined axial compression, radial shear, and overturning moment simultaneously. Axial loads result from structural weight and supported equipment mass. Radial forces are generated by wind, dynamic movement, or lateral offset forces. Overturning moment arises when the center of gravity is offset from the rotational axis.
Engineers calculate equivalent dynamic bearing loads using combined load formulas that incorporate axial and radial factors. Proper bolt grade selection and flange thickness design ensure that mounting stress remains within allowable limits.
| Parameter | Design Impact | Engineering Consideration |
| Axial Load Capacity | Determines vertical support limit | Bearing ball or roller diameter |
| Moment Capacity | Prevents tilting deformation | Flange width and bolt spacing |
| Radial Stability | Controls lateral displacement | Raceway geometry optimization |
Material Selection and Heat Treatment
Material strength is essential for long-term performance. Slewing ring components are commonly manufactured from high-strength alloy steel with induction-hardened raceways. The internal gear teeth undergo quenching and tempering processes to increase surface hardness while maintaining core toughness.
Controlled heat treatment prevents distortion that could affect gear meshing accuracy. Surface hardness levels are balanced to achieve wear resistance without brittleness. Protective coatings such as phosphating or painting reduce corrosion risk in outdoor installations.
Sealing Systems and Environmental Protection
Vertical internal gear slewing drives frequently operate in exposed environments including construction sites, renewable energy fields, and port facilities. Sealing systems prevent dust, water, and debris from entering the bearing raceways and gear engagement area.
Elastomer sealing rings are installed between rotating rings, forming a barrier against contaminants. In marine or high-humidity environments, additional corrosion-resistant coatings and stainless fasteners may be integrated into the assembly.
- Dual-lip sealing configuration for enhanced protection
- Grease retention grooves along raceways
- Drainage paths to prevent moisture accumulation
Installation Guidelines for Structural Stability
Accurate installation directly affects performance. Mounting surfaces must meet flatness tolerance requirements to avoid uneven stress distribution. Bolt tightening procedures follow calibrated torque sequences to achieve uniform preload across the flange.
During assembly, gear meshing alignment is verified through contact pattern testing. After installation, rotation testing under no-load conditions confirms smooth movement without binding or abnormal noise.
Maintenance and Service Life Optimization
Preventive maintenance extends service life and maintains torque accuracy. Regular lubrication intervals are determined by operating hours, environmental conditions, and load intensity. Grease replenishment prevents metal-to-metal contact and reduces wear.
Periodic inspection includes checking bolt torque, gear backlash, seal integrity, and surface corrosion. Early detection of wear patterns allows timely corrective action before structural damage occurs.
Industrial Applications of Vertical Internal Gear Slewing Drives
Vertical internal gear slewing drives are widely integrated into equipment requiring stable rotation under heavy load. In tower cranes and lifting machinery, they support rotating superstructures while maintaining structural stability. In solar tracking systems, they provide controlled angular adjustment to optimize energy capture throughout the day.
Material handling systems use these drives to rotate conveyor platforms and robotic arms. In port machinery and offshore installations, the internal gear configuration reduces exposure to harsh environmental elements, improving operational reliability.
By combining enclosed gear protection, high torque density, and robust load-bearing capability, vertical internal gear slewing drives deliver dependable rotational performance across construction, renewable energy, marine, and industrial automation sectors.