How do lubrication and sealing requirements differ for vertical internal gear designs?
 2025.08.22
2025.08.22
 Industry news
Industry news
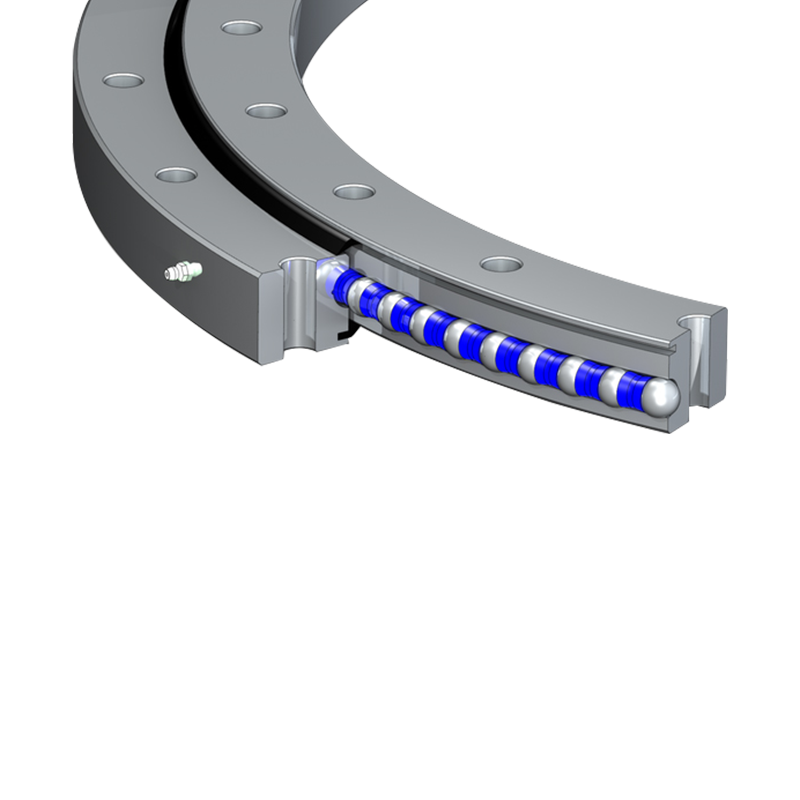
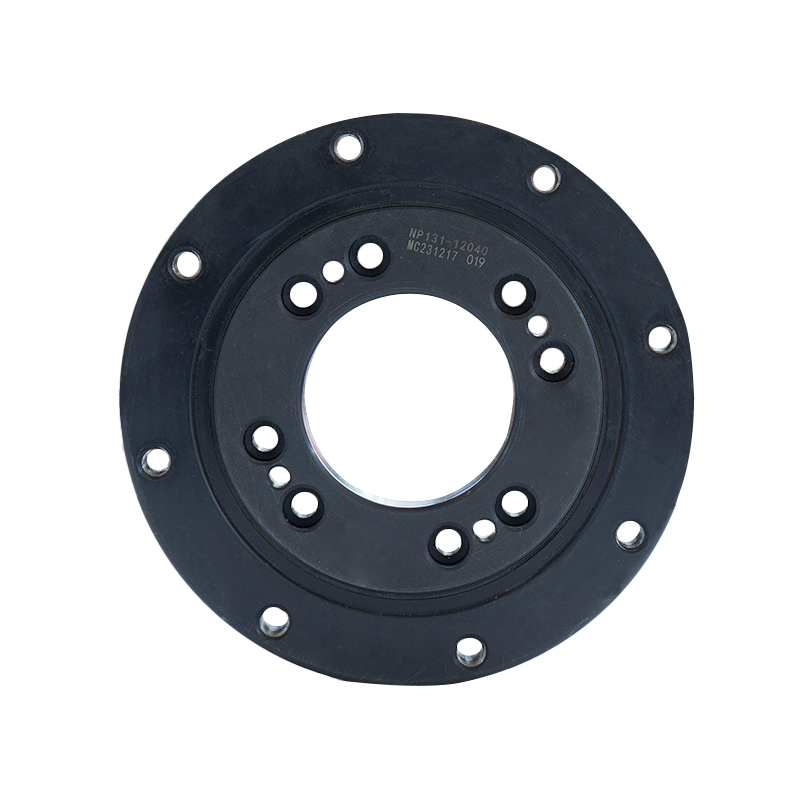
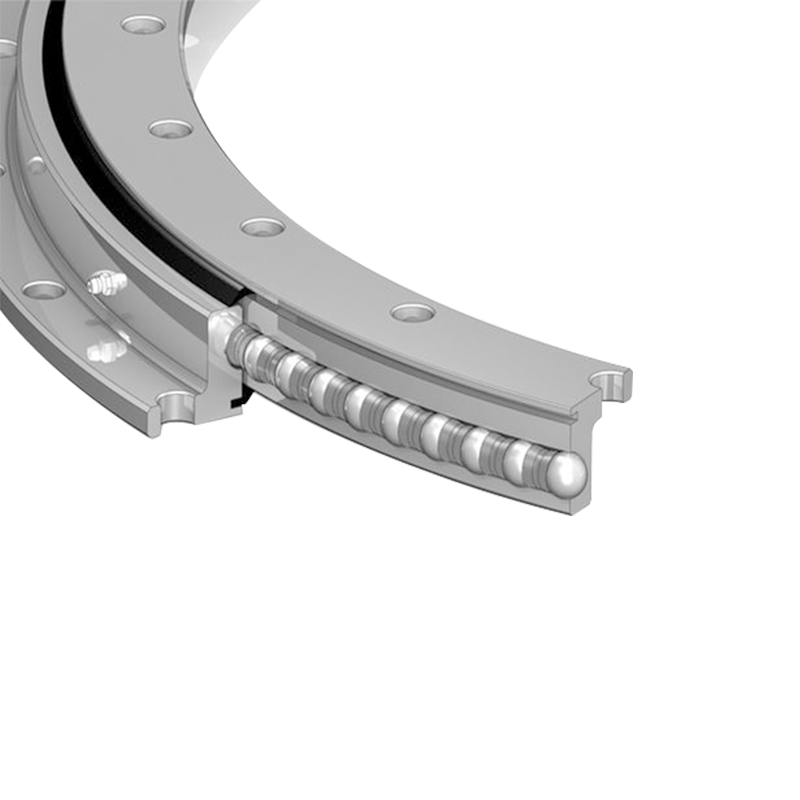
Vertical internal gear slewing drives have unique operating conditions compared with external gear or horizontally mounted systems, and these differences directly influence how lubrication and sealing should be managed. The vertical orientation changes the way loads are distributed, how lubricants behave inside the housing, and how effectively the system can be protected against leakage and contamination.
Lubrication Requirements
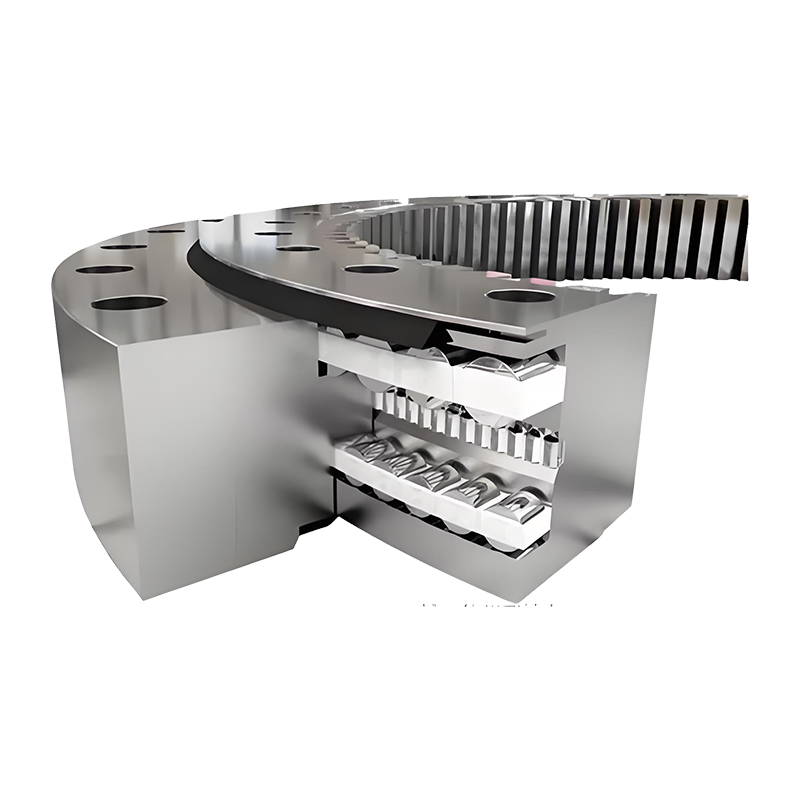
In a vertical slewing drive, gravity plays a significant role in how grease or oil settles within the housing. Unlike horizontal drives, where lubricant can spread more evenly, vertical drives tend to cause lubricants to drain toward the lower part of the assembly. As a result, the upper sections of the gear mesh and bearing surfaces may not always receive sufficient coverage. To address this, manufacturers often recommend lubricants with higher viscosity or enhanced adhesive properties, which help form a stable film that resists downward flow. Some designs also incorporate circulation paths or grease channels to ensure that lubricant reaches every critical contact point.
Because of this uneven distribution risk, inspection intervals for lubrication tend to be shorter in vertical applications. Operators must confirm that all sections of the drive remain properly lubricated and that the lubricant has not degraded prematurely due to heat, load, or environmental exposure.
Sealing Requirements
Sealing performance is equally important in vertical internal gear slewing drives. In these systems, leakage risk exists both at the lower seals, where lubricant tends to collect, and at the upper seals, where negative pressure or splash can lead to gradual seepage. To counter these issues, advanced sealing systems such as multi-lip seals, labyrinth seals, or customized dust-proof structures are often employed.
Another advantage of the internal gear design is that the gears are positioned within the housing, which offers some inherent protection against external contaminants. However, dust, moisture, and abrasive particles can still find their way inside if the seals are compromised. This makes seal integrity a critical factor in maintaining long-term reliability. Regular monitoring is necessary to detect signs of leakage or contamination early, preventing damage to the gears and bearings.
Conclusion
The vertical orientation and internal gear configuration of these slewing drives create distinct challenges for lubrication and sealing. Ensuring consistent lubricant coverage across all working surfaces and maintaining robust seals against leakage and contamination are key factors in achieving reliable operation. With the right choice of lubricants, careful attention to seal design, and proactive maintenance practices, vertical internal gear slewing drives can deliver long service life even under demanding conditions.